Hello Readers,
This is part 3 of the 5-part Series on cracking the AWS Solutions Architect - Associate Exam. Click here for part 2 - AWS EC2.
I've divided the notes into a 5 part series.
- Part 1: Introduction and AWS S3
- Part 2: AWS EC2
- Part 3: Databases
- Part 4: DNS, VPC, and HA(High-Availability)
- Part 5: Application Services and Serverless + Bonus
Database Notes
Database in AWS:
- RDS (OLTP-Online transaction processing) - Ex: give order ID, returns all data
- SQL Server
- Oracle
- MySQL Server
- PostgreSQL
- Aurora
- MariaDB
- NoSQL
- DynamoDB
- Data Warehouse (OLAP-Online analytical processing) - For complex analytics & BI.
- Redshift
Elasticache - improves the performance of DB by caching frequent queries.
- Two types
- Memcache
- Redis
- You can set up an Autoscaling group that can auto-scale Cache nodes based on CPU usage.
- Two types
Key Features of RDS
- Multi-AZ - For disaster recovery
- Read Replicas - For Performance ( Max 5 copies for a DB )
Types of RDS backups
- Automated Backups
- point-in-time recovery;
- Retention period - 1 to 35 days;
- Backups stored in S3 (for free)
- Takes 1 daily snapshot and transactional logs.
- These are deleted when RDS is deleted
- Database Snapshots
- Manual snapshots
- These are NOT deleted when RDS is deleted
General RDS Notes
- [NEW] You can autoscale using RDS Auto Scaling groups
- Two ways to cope with heavy DB load - Elasticache & Read replica
- Read replica is mainly for Performance
- Multi-AZ is mainly for Disaster Recovery
- Cross-region Read replica can be created for Disaster Recovery
DynamoDB
- Stored on SSD - Hence fast
- Spread across 3 AZ
- DynamoDB allows for the storage of large text and binary objects, but there is a limit of 400 KB.
- Has DAX(DynamoDb Accelerator) - in-memory cache(for performance) - It is similar to Elasticache for RDS.
- Two types:
- Eventual consistency Read (default) - takes around 1 second to update
- Strong consistency Read - updates Within 1 second and can be read
RedShift
- Single Node ( 160Gb )
- Multi-Node
- Leader Node (manages client connection and received requests)
- Compute Node (Stores data and performs computations). Up to 128 nodes.
- Has Advanced Compression -Columnar compression(data in the column is of the same type)
- Massively Parallel Processing (MPP)
- Backups are taken by default with 1-day retention. & Max = 35 days (similar to RDS)
- It maintains 3 copies of data - Original & Replica on the compute node. Backup in S3.
- Charged only for compute node - Not for Leader node
- No multi-AZ support. It can only be in 1 AZ.
Aurora
- Start with 10GB. Scales in 10Gb Increments. Up to 64TB
- Compute resource up to 32vCPUs and 244Gb of memory
- 2 copies in each AZ. Minimum of 3 AZ. So 6 copies of your data.
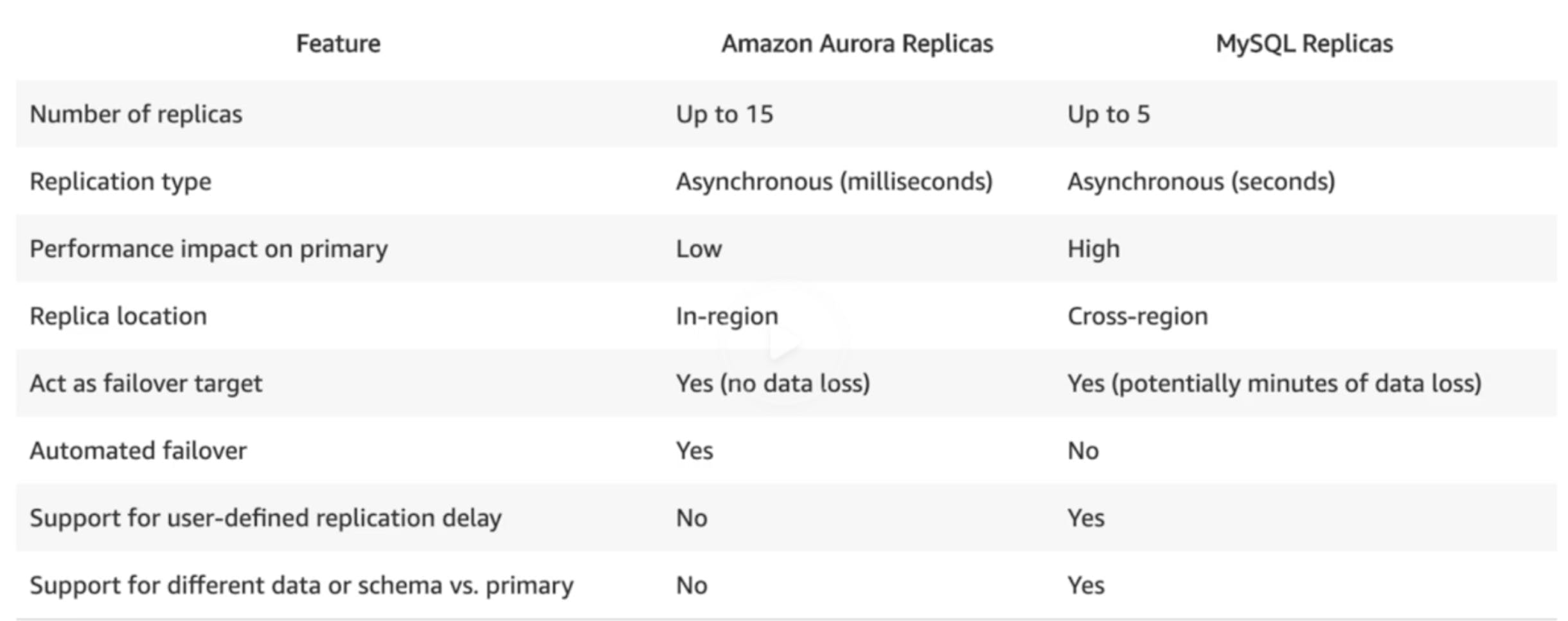
- Types of Aurora replicas:
- Aurora Replicas (max 15)
- MySQL Read Replicas (max 5)
- PostgreSQL (max 1)
Aurora Serverless
- Simple Cost-effective option for infrequent, intermittent, or unpredictable workloads
- Automatically start-up shut down, and scale capacity up or down based on your application's needs
Continue reading Part 4 - AWS Route53, VPC, and HA ...